Persian Miniature Painting: The Detailed and Historic Art Form
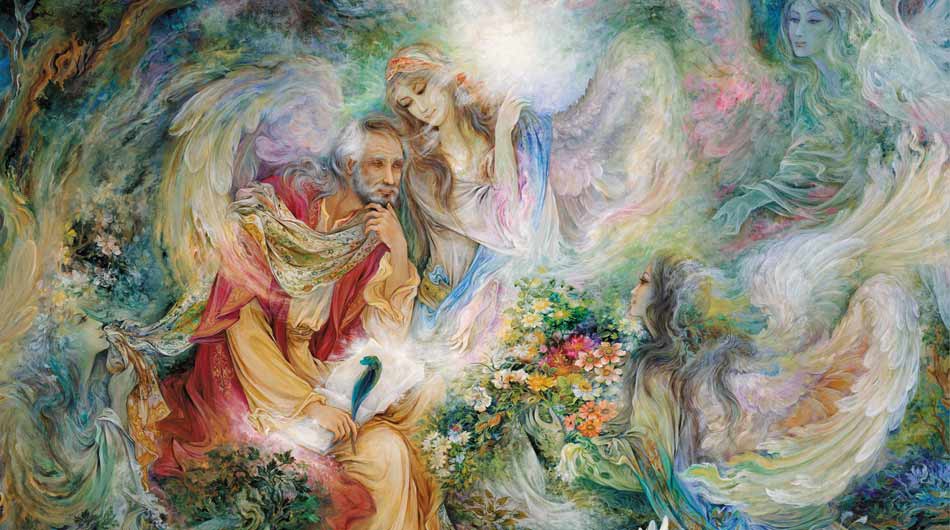
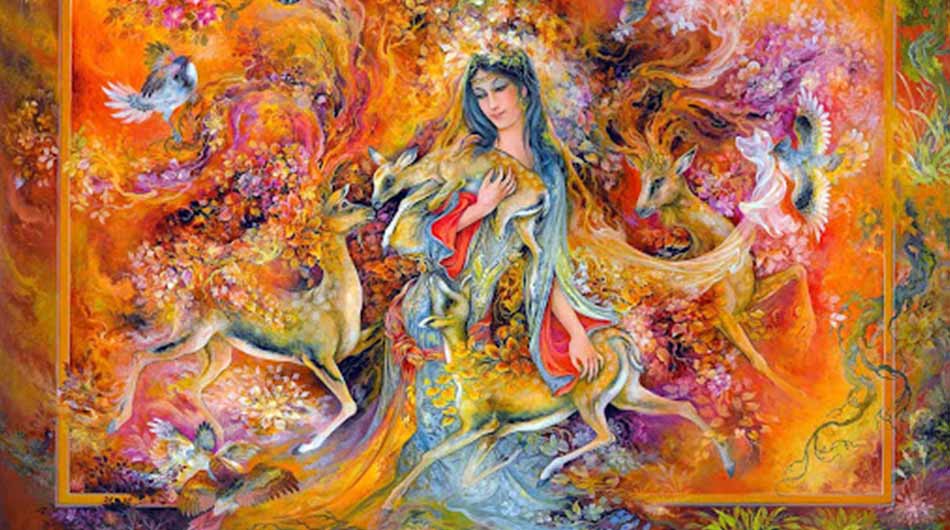
Persian miniature painting is a richly detailed and historic art form that has been an integral part of Persian culture for centuries. This exquisite genre of painting, characterized by its intricate designs, vivid colors, and meticulous attention to detail, offers a glimpse into the artistic, cultural, and historical narratives of Persia. From its origins to its evolution, Persian miniature painting stands as a testament to the sophistication and creativity of Persian artists.
Origins and Historical Context
The roots of Persian miniature painting can be traced back to the early Islamic period, around the 9th century, although it truly flourished between the 13th and 16th centuries. This art form evolved alongside the Persian manuscript tradition, often adorning the pages of illuminated manuscripts and serving as visual narratives to accompany literary texts. The art of the miniature reached its zenith during the Ilkhanid, Timurid, and Safavid dynasties, each of which contributed to its stylistic development.
The Ilkhanid period (1256-1353) marked the beginning of a more sophisticated and detailed approach to miniature painting. Influenced by Chinese artistic traditions brought by the Mongol rulers, Persian artists began to incorporate elements such as detailed landscapes and naturalistic figures. This era laid the foundation for the flourishing of miniature painting in the subsequent centuries.
During the Timurid era (1370-1507), Persian miniature painting reached new heights of refinement. The Timurids were great patrons of the arts, and under their rule, the Herat School of painting emerged. This school is renowned for its intricate compositions, delicate brushwork, and the use of vibrant colors. The Timurid period saw the creation of some of the most celebrated Persian manuscripts, including the “Shahnama” (Book of Kings) and the “Khamseh” (Quintet) of Nizami, which featured exquisite miniature illustrations.
The Safavid Era and Its Innovations
The Safavid dynasty (1501-1736) is often regarded as the golden age of Persian miniature painting. Under the patronage of Shah Ismail I and Shah Tahmasp I, the art form reached unparalleled levels of sophistication and elegance. The Safavid period saw the rise of the Tabriz and Isfahan schools of painting, each contributing to the diversity and richness of Persian miniatures.
The Tabriz School, established by Shah Ismail I, is known for its dynamic compositions and expressive figures. One of the most famous works from this school is the “Shahnameh of Shah Tahmasp,” a monumental manuscript that showcases the pinnacle of Persian miniature art. The miniatures in this manuscript are characterized by their intricate details, vibrant color palette, and a harmonious blend of Persian and Chinese artistic elements.
The Isfahan School, which flourished under Shah Abbas I, introduced a more naturalistic and less stylized approach to miniature painting. This period saw the emergence of master painters such as Reza Abbasi, whose works are celebrated for their delicate lines, elegant figures, and subdued color schemes. The Isfahan School also emphasized the depiction of everyday life, moving away from the traditional themes of epic poetry and courtly life.
Techniques and Characteristics
Persian miniature painting is distinguished by its meticulous techniques and distinctive characteristics. Artists used fine brushes made from squirrel hair to achieve the intricate details that define this art form. The miniatures were painted on various surfaces, including paper, parchment, and ivory, using natural pigments derived from minerals, plants, and insects. Gold and silver leaf were often used to enhance the luminosity and richness of the paintings.
The compositions of Persian miniatures are highly detailed and often filled with intricate patterns and motifs. Figures are depicted with elongated proportions and delicate features, adorned in elaborate costumes that reflect the fashion of the time. The backgrounds are richly decorated with intricate floral designs, geometric patterns, and architectural elements, creating a sense of depth and complexity.
Color plays a crucial role in Persian miniature painting. Artists employed a vivid and harmonious color palette, with each hue carefully chosen to enhance the overall composition. The use of bold colors, such as lapis lazuli blue, vermilion red, and gold, adds a sense of vibrancy and opulence to the miniatures.
Cultural and Artistic Significance
Persian miniature painting is not just an artistic expression but also a reflection of Persian culture and history. The miniatures often illustrate scenes from Persian literature, mythology, and history, providing a visual narrative that complements the written text. The “Shahnama” and the works of poets like Ferdowsi, Hafez, and Nizami are among the most popular sources of inspiration for Persian miniaturists.
Moreover, Persian miniatures offer insights into the social and cultural life of the time. The detailed depictions of courtly life, hunting scenes, and festive gatherings provide a glimpse into the customs, traditions, and daily activities of Persian society. The art form also serves as a testament to the patronage of Persian rulers, who supported and nurtured the development of this exquisite genre.
Legacy and Contemporary Influence
The legacy of Persian miniature painting continues to influence contemporary art and culture. While the traditional techniques and themes are still practiced by modern artists, there is also a growing interest in reinterpreting this historic art form through contemporary lenses. Exhibitions, workshops, and academic studies dedicated to Persian miniatures ensure that this rich artistic tradition remains vibrant and relevant in the modern era.
In conclusion, Persian miniature painting is a timeless and intricate art form that encapsulates the beauty, sophistication, and cultural heritage of Persia. Its detailed compositions, vibrant colors, and historical significance make it a treasured legacy that continues to inspire and captivate art enthusiasts around the world.
Tags:Adventure holidays, Best time to travel to iran, best tour operator iran, Cultural sites of Iran, Culture of Iranian People, Economy of Travel, Holiday in Iran, Iran, Iran Architectural, iran attractions, Iran country, Iran cultural, iran destinations, Iran enriching experience, Iran sightseeing tours, iran Solo trip, iran tour, Iran tour packages, iran tourist attractions, Iran travel agency, iran travel expenses, Iran Travel Guide, Iran Travel Tips, Iranian culture, must-visit Iran, persia tour, Persian miniature painting, Surfing In Iran, top tourist destinations, travel to iran, Traveling to Iran, travelling to iran, trip to iran, vacation packages, visit iran, درناگشت